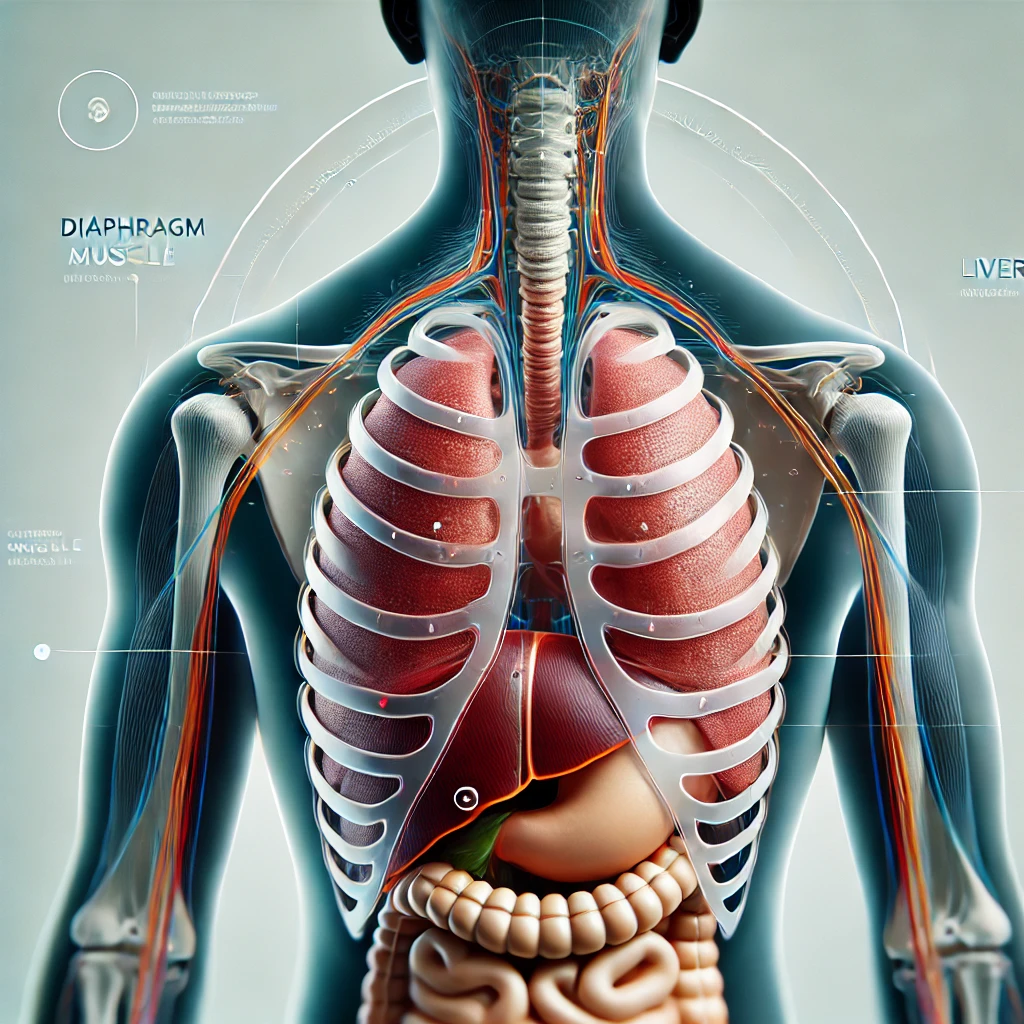
What causes Hemidiaphragmatic Elevation?
Elevation of the semi-diaphragm causes restriction in the chest, preventing full ventilation of the lungs. This phenomenon can be either congenital or occur as an acquired disorder. The effects of elevation vary depending on the severity, from mild dyspnea to chronic respiratory failure in severe cases.
Causes of Hemidiaphragm Elevation
Causes of hemiplegia may include:
- Phrenic Nerve Damage: Damage or paralysis of the phrenic nerve can cause hiccups, as the diaphragm loses the ability to function normally on the affected side.
- Surgical Procedures: After thoracic or cardiac surgery, the diaphragm may become elevated due to temporary or permanent tissue or nerve injury.
- Pneumothorax or Pleural Effusion: In cases where air or fluid accumulates around the lungs, the pressure exerted can lead to elevation of the diaphragm.
- Tumors or Benign Tumors of the Chest: The pressure exerted by tumors on the diaphragm can also lead to elevation and rare diseases that resemble tumors, such as large cysts, such as generalized thoracic echinococcosis.
Symptoms of Hemiplegia
Symptoms associated with hemiparesis include:
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing: Limited diaphragm movement can cause chronic shortness of breath, especially during exercise or even simple movements such as bending over to tie our shoelaces.
- Fatigue: Difficulty breathing can cause fatigue, as the body does not receive enough oxygen.
- Chest or Back Pain: Pressure and changes in the structure of the chest can cause pain or discomfort.
- Reduced Respiratory Function: In more severe cases, elevation can affect lung function and lead to respiratory failure.
Diagnosis of Hemidiaphragmatic Elevation
The diagnosis of hemiparesis includes a clinical examination and a series of imaging tests:
- Chest X-ray: Usually reveals the position of the diaphragm and helps identify the elevation.
- Ultrasound or CT scan tomography: Allows detailed visualization of the diaphragm area and can identify any causes of pressure, such as tumors or fluid in the chest.
- Electromyography: Used to evaluate the function of the phrenic nerve and diaphragm.
- Radiography: Under direct fluoroscopy, a functional check of the function of the semi-diaphragm is performed, as well as the "paradoxical mobility" of the semidiaphragm, i.e. its abnormal movement during breathing.
Treatment Options
For patients with severe hemiparesis who are experiencing severe symptoms, surgical treatment is often the best option. Modern surgical techniques include innovative approaches, such as robotic diaphragm folding (Robotic Plication of the Hemidiaphragm), which allow for safe and precise surgery, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring better restoration of respiratory function.
Conclusion
Elevated hemiparesis is a condition that can significantly affect quality of life, especially when it causes respiratory difficulties. Early diagnosis and collaboration with a specialized thoracic surgeon are crucial for choosing the appropriate treatment and improving respiratory function. Modern techniques, such as robotic surgery, offer excellent possibilities for safe and effective treatment of the most serious cases.